Companion diagnostics (CDx) is used as a companion to a therapeutic agent to determine its applicability (e.g. predict response to therapy, toxicity...) to a specific person. Commonly, companion diagnostics is named as one of the hallmarks of "precision medicine". Let's look a bit closer at the current state of this exciting segment of diagnostics.
Indications
What indications is companion diagnostics currently used for? As of 2020, all but one (used for hematology) of 44 FDA-approved CDx tests were utilized for drugs targeting oncology indications. This number grew to 50 as of April 2022 and one more non-oncology indication, POMC/PCSK1/LEPR panel for obesity. Indeed, oncology has been tightly connected with companion diagnostics.
Immunohistochemistry (IHC) assay HercepTest™ was approved by FDA in September 1998 for the detection of HER2 protein expression in tumour tissue to aid therapy with trastuzumab. HercepTest™ was the first companion diagnostic ever approved by the FDA, and more than 20 years of use has documented its clinical impact. Importantly, certain biomarkers such as PD-L1 have been heavily targeted and will likely continue to be targeted due to their implications in therapy response of checkpoint inhibitors used in a variety of oncology indications.
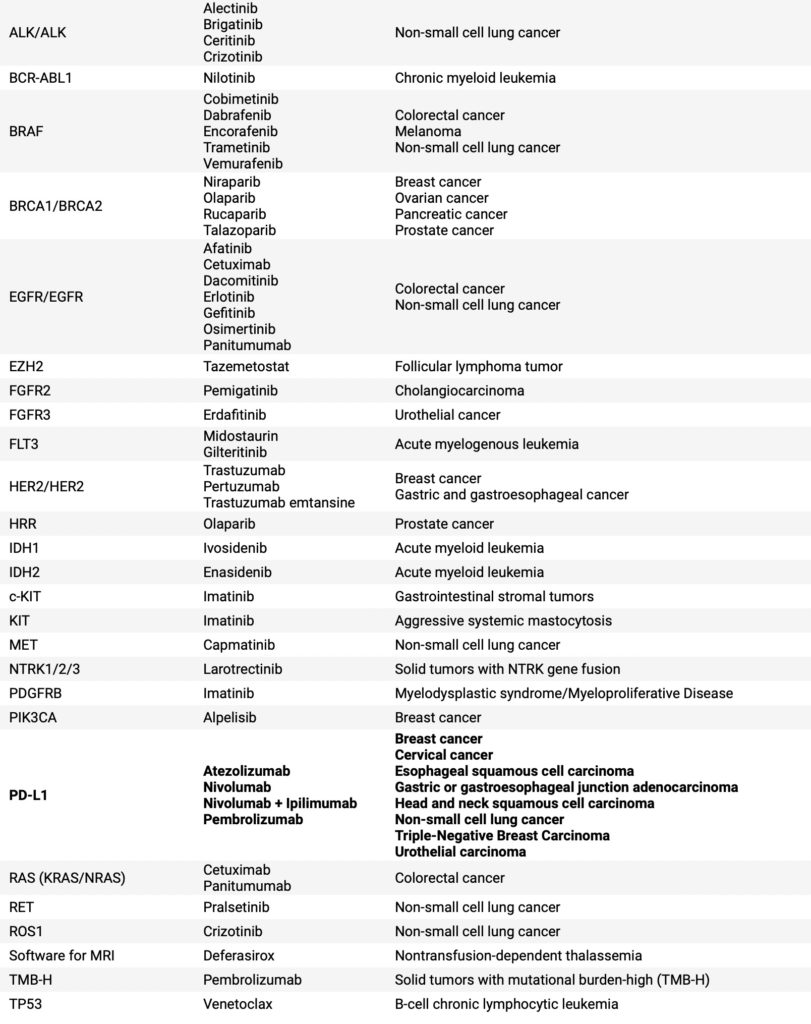
Table 1: Overview of biomarkers analyzed, drug molecules and their indications of FDA-approved CDx assays until 2020 (adapted from review by Jan Trøst Jørgensen).
Technology platforms
Looking at the history of technology platforms for the different CDx assays, unsurprisingly IHC and in situ hybridization (ISH) were the dominating technologies until the end of 2000s. Beginning with 2011, the first PCR-based BRAF V600 Mutation Test was approved. Since then the share of PCR-based CDx assay has grown to represent currently the largest (36%) portion of all FDA-approved CDx assays. Increasingly, NGS is becoming the method of choice for the newest approved tests.
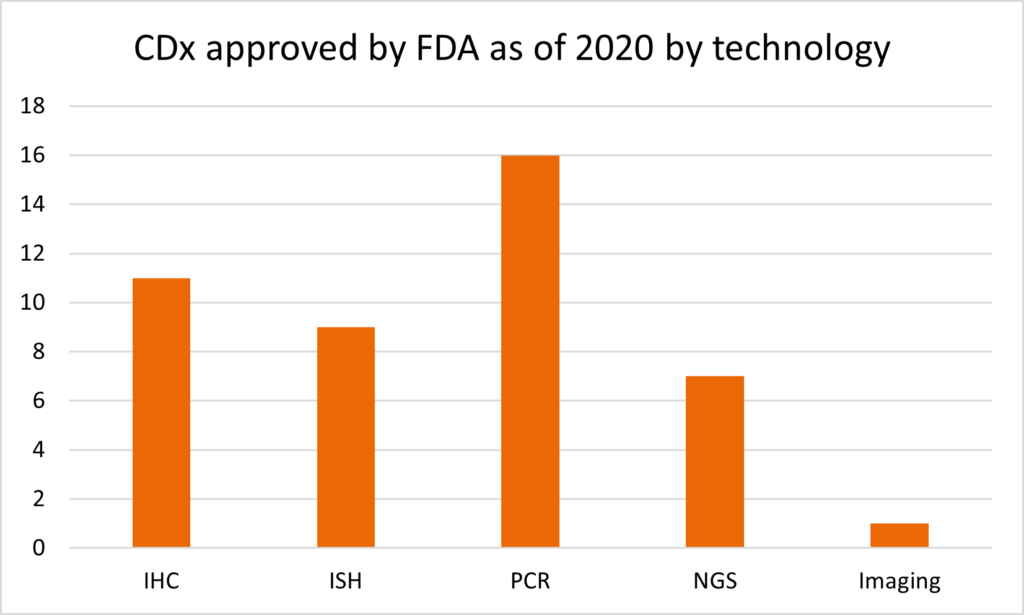
Table 2: Overview of the CDx by the technology utilized (adapted from review by Jan Trøst Jørgensen).
Regulatory affairs
There is generally a high level of congruence between EMA and FDA for medicinal products that require a CDx, since the therapeutic indications granted by both agencies are often identical or very similar, applications for medicinal products are usually reviewed in parallel, share the same developer and are based on the same or similar evidence and therefore the same diagnostic tests are used in the pivotal clinical trials.
However, in the EU, the regulatory assessment process for CDx is currently disconnected from the regulatory process of its corresponding drug, and follows the regulatory requirements of in vitro diagnostic medical devices. Nevertheless, with the IVDR (EU) 2017/746 coming into full force in May 2022, medicines regulatory authorities, including EMA assume a responsibility in reviewing the “suitability” of the CDx in conjuction to the corresponding drug.
Importantly, most CDx assays in the USA are typically classified as high-risk devices of Class III, which neccessitates to take the regulatory route of a Premarket Application (PMA). Compared to other types of typical IVD submissions such as the 510(k) procedure, the PMA requires much more thorough level of documentation. On the other hand, IVDR will bring risk stratification (A, B, C and D) to Europe. CDx devices should be classified as risk class C (High patient risk and/or moderate public health risk), and be subject to a conformity assessment carried out by a Notified Body.
Outlook
- According to Emergen Research, the global companion diagnostics market size was USD 2.43 billion in 2019 and is expected to reach USD 9.72 billion in 2027, thus attain a revenue CAGR of 18.3% during the forecast period.
- Between 2011 and 2020, there were an average of 3.5 companion diagnostics tests approved yearly by FDA, compared to an average of 0.7 between 1998 and 2010. We can expect oncology indications to dominate the space for the foreseeable future.
- In addition to assessing therapy response, CDx also play an increasingly important role as Clinical Trial Assays (CTAs) in streamlining clinical trial participant selection. The aim is to select for responders to have a greater chance of meeting the clinical endpoints and statistical significance.
- NGS as a technology platform is likely to play an increasingly important role and we expect it to dominate the segment within the 5-7 year timeframe.
- EU regulatory changes instigated by IVDR will have significant impact on the development and assessment of CDx solutions; Risk classifcation, drug regulators involved in the assessment of CDx, etc.
Get in touch at info@ambiom.com to find out how we can work together in this space.
Sources:
https://aabme.asme.org/posts/companion-diagnostics-for-oncology
https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/documents/presentation/presentation-health-technology-assessment-companion-diagnostics_en.pdf
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1936523321000553
https://www.fda.gov/medical-devices/in-vitro-diagnostics/list-cleared-or-approved-companion-diagnostic-devices-in-vitro-and-imaging-tools
https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fonc.2021.676939/full
https://www.tuv.com/world/en/companion-diagnostics-(in-vitro-diagnostics-cdx).html
No comments.